A combination Revolution
Amid a KRAS data dump, a doublet of RMC-6236 and RMC-6291 was a highlight.
Amid a KRAS data dump, a doublet of RMC-6236 and RMC-6291 was a highlight.

Revolution Medicines aims to do better than the KRAS inhibitor incumbents, and the group reported a raft of data on Monday that, it believes, show it to be on the right track. Probably the most interesting update came from a combination of the pan-KRAS inhibitor RMC-6236 and the G12C selective project RMC-6291 that, in late-line colorectal cancer, produced an ORR of 25%.
However, investors sent Revolution’s stock down 10% on Monday. Perhaps its backers were looking for more impressive signs of efficacy from combo data of what is the most advanced asset belonging to a company worth almost $9bn.
No escape?
Revolution’s claim to fame is that its projects target the “on” states of KRAS proteins; according to the company it is RAS “on” signalling that drives uncontrolled growth, so it believes that its assets could have the edge over KRAS “off” inhibitors such as Amgen’s Lumakras and Bristol Myers Squibb’s Krazati.
And the idea behind combining the pan-KRAS and G12C inhibitors is to prevent tumour-escape mechanisms. However, one question is why this can’t be addressed with a pan-KRAS inhibitor alone.
Revolution reported an ORR of just 9% with RMC-6236 monotherapy in RAS inhibitor-naive CRC patients, while RMC-6291 led to an ORR of 0% in patients who’d previously received a KRAS G12C “off” inhibitor such as Amgen’s Lumakras.
The 25% ORR seen with the doublet, among 12 patients previously treated with a KRAS G12C “off” inhibitor, looks unimpressive on the face of it, bit it's an improvement over these numbers. It’s also better than the historical 1-6% that Revolution cited with chemo in late-line CRC.
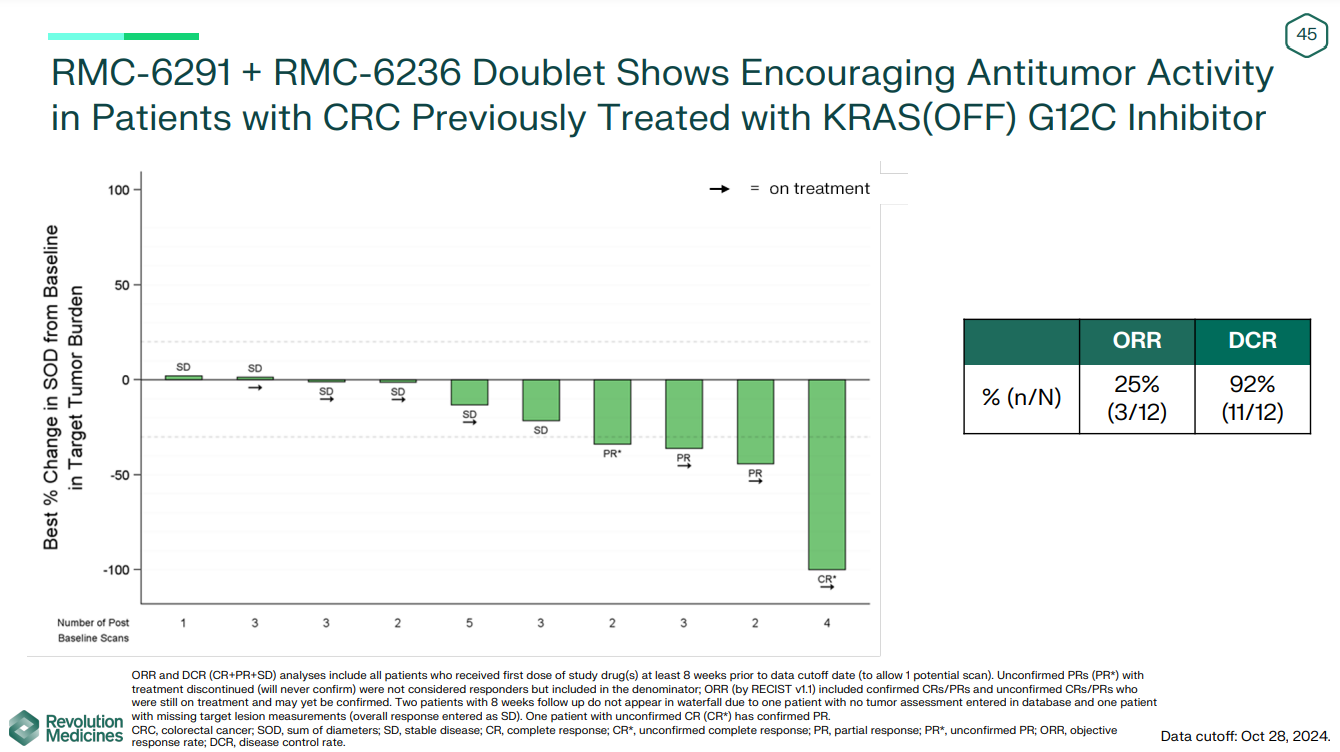
However, patient numbers are small, and Revolution didn’t report any efficacy data with the doublet across other cancers enrolled in the phase 1 study, including NSCLC and pancreatic cancer.
As for adverse events, low-grade rash and diarrhoea were most common, although there was one report of grade 4 hypokalemia linked with grade 3 diarrhoea.
Revolution plans to evaluate the doublet further, and on a conference call on Monday said it hoped to study a triplet of RMC-6236, RMC-6291 and Keytruda in first-line NSCLC.
NSCLC plans
The group has more immediate goals in NSCLC, namely to begin Rasolve-301, a phase 3 trial of RMC-6236 in previously treated disease. Today the company said this would enrol around 400 patients who have received one or two prior lines of therapy, excluding docetaxel.
Subjects will be randomised to either RMC-6236 or docetaxel, and endpoints will include PFS and OS. The primary analysis will involve patients with RAS G12X mutations (excluding G12C). The extended population will incorporate other RAS mutations, including G12C, G13X or Q61X.
Notably, in NSCLC Revolution is planning to test 200mg daily – versus 300mg daily in pancreatic cancer, where the phase 3 Rasolute-302 study recently began. This is because of a “less favourable” tolerability profile with the 300mg dose in NSCLC, the company said, suggesting that lung cancer patients were less tolerant of adverse events.
2586













